JavaScript基础:为初学者学习 JavaScript 中的数据结构
介绍
它是 JavaScript 中学习数据结构的注释。我研究了长途跋涉的Github 存储库的源代码表单。对于JavaScript开发人员和初学者来说,这是一个很好的材料来学习数据结构。
除了Trekhleb的 Github, 我还提到《离开: 乌迪米编程和编码采访》和哈克兰克的视频。本课程使用 Java 实现和解释数据结构。
本文总结并包括以下数据结构。
下表显示了常见操作的时间复杂性。堆栈和队列的实现基于链接列表。它们允许用户有效地插入或删除节点。
为了具有更好的遍历整个容器的性能,我们可以考虑使用哈希表或二进制搜索树。这取决于您是否要订购数据。
+—+—————–+—————–+—————–+ | | Insert | Delete | Traverse | +—+—————–+—————–+—————–+ | 1 | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | | 2 | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | | 3 | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | | 4 | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | | 5 | O(1)~O(n) | O(1)~O(n) | O(1)~O(n) | | 6 | O(log n)~O(n) | O(log n)~O(n) | O(log n)~O(n) | | 7 | O (log n) | O (log n) | O(n) | +—+—————–+—————–+—————–+
1. 链接列表
单个链接列表是单向列表。
链接列表的优点是允许用户在恒定时间有效地插入或删除节点。
但是,链接列表不善于访问数据。我们不允许访问链接列表中具有索引的数据。我们只能通过遍历容器来查找目标数据。
+————-+———-+———+———-+——————-+ | operations | Insert | Delete | Traverse | Search and Delete | +————-+———-+———+———-+——————-+ | complexity | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | +————-+———-+———+———-+——————-+
在本节中,我参考源代码Trekhleb的 Github,并用我个人的想法进行一些修改。
JavaScript 中的实现
- 在 JavaScript 中创建链接列表结构
单个链接列表具有头节点和尾部节点。每个节点都有一个值字段和一个指向下一个节点的指针

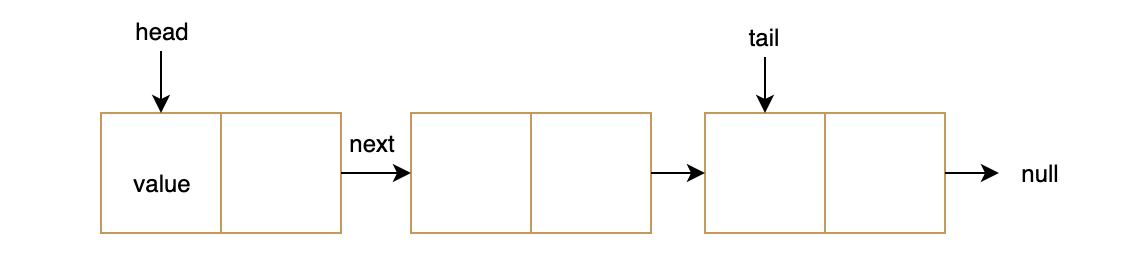
复制right@A莱曼
数据结构的实现:
class Node {
constructor(value = null) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
}
2.插入
有两种不同的方法来插入新节点。
- 将新节点放在尾部节点后面。如果我们没有尾节点指针,我们必须转到链接列表的末尾。
- 时间复杂性为 O(1) 或 O(n)。这取决于我们如何实现链接列表。

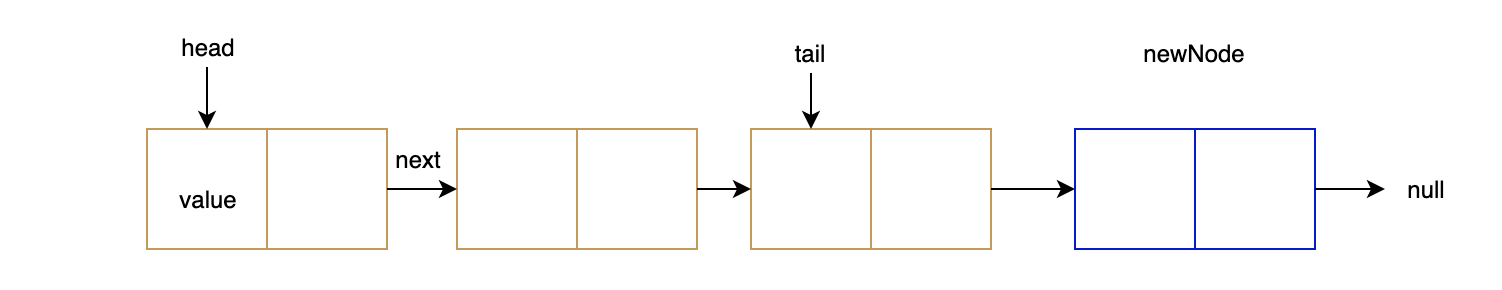
复制right@A莱曼
append(value) {
const newNode = new node(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
return this;
}
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
return this;
}
- 从头节点插入新节点(复杂性:O(1))
prepend(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.next = this.head
this.head = newNode;
if (!this.tail) {
this.tail = newNode;
}
return this;
}
3.删除头节点(复杂度:O(1))
deleteHead() {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}const delete = this.head;
if (this.head.next) {
this.head = this.head.next;
} else {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}return delete;
}
4.搜索/访问/遍历(复杂度:O(n))
浏览整个列表并返回目标节点,目标值或回调函数返回 true
find({value = undefined, callback = undefined}) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode && currentNode.next) {
if (callback && callback(currentNode.value)) {
return currentNode;
}if (currentNode.value === value) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return null;
}
5.搜索和删除(复杂性:O(n))
删除操作必须遵循这些顺序,因为链接列表没有指向上一个节点的指针。
- 如果值等于目标值,则删除头节点
- 如果值等于目标值,则删除直接节点
- 如果值等于目标值,则删除尾部节点
delete(value) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
//Check the head node if the value is the target value
let deletedNode = null;
if (this.head.value === value) {
deletedNode = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
}
//Check immediate node if the value is the target value
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode.next) {
if (currentNode.next.value === value) {
deletedNode = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next = currentNode.next.next;
} else {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
//Check the tail node if the value is the target value
if (this.tail.value === value) {
this.tail = null;
}
return deletedNode;
}
引用
2. 双链接列表
双链接列表是双向列表。它有一个额外的指针,称为上一个指针来链接上一个节点。链接列表和双重列表之间的主要区别是搜索和删除操作。
+————-+———-+———+———-+——————-+ | operations | Insert | Delete | Traverse | Search and Delete | +————-+———-+———+———-+——————-+ | complexity | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | +————-+———-+———+———-+——————-+
在本节中,我参考Trekhleb的 Github 上的源代码,并用我个人的想法进行一些修改。
JavaScript 中的实现
1.在 JavaScript 中创建链接列表结构
双链接列表具有头和尾部节点。节点具有一个值、指向下一个节点的指针以及指向上一个节点的上一个与链接列表不同的上一个节点的指针。

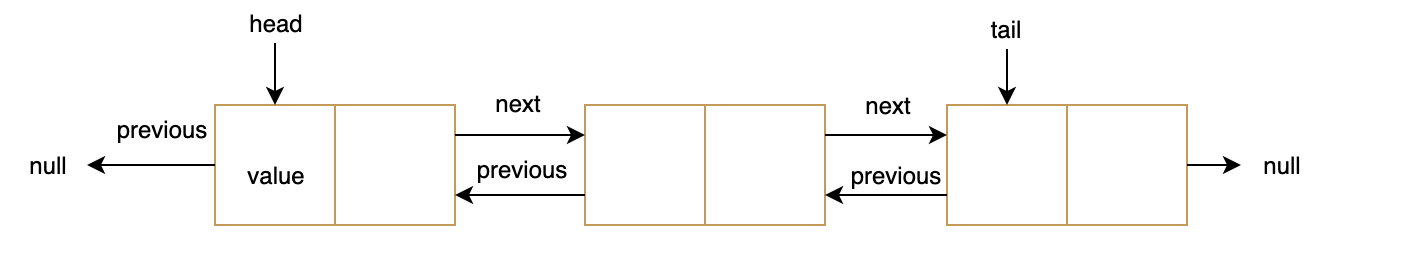
复制right@A莱曼
class Node {
constructor(value = null) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
**this.previous = previous;**
}
}class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
}
2.插入(复杂度:O(1))
有两种不同的方法来插入新节点。
- 将新节点放在尾部节点后面。它与链接列表相同。区别在于将新节点的上一个指针设置为尾部节点。
append(value) {
const newNode = new node(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
return this;
}
this.tail.next = newNode;
**newNode.previous = this.tail; **
this.tail = newNode;
return this;
}
- 从头节点插入新节点。它与链接列表相同。区别在于将头节点的上一个指针设置为新节点。
prepend(value) {
const newNode = new LinkedListNode(value);
newNode.next = this.head
**if (this.head) {
this.head.previous = newNode;
}**
this.head = newNode;
if (!this.tail) {
this.tail = newNode;
}
return this;
}
3.从头部删除(复杂度:O(1))
区别在于将头节点的上一个指针设置为 null。
deleteHead() {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}const delete = this.head;
if (this.head.next) {
this.head = this.head.next;
**this.head.previous = null;**
} else {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}return delete;
}
4.搜索/访问/遍历(复杂度:O(n))
它与链接列表相同
5.搜索和删除(复杂性:O(n))
与链接列表不同,删除操作不必遵循顺序,因为双链接列表具有上一个指针。
delete(value) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
//Check the head node if the value is the target value
let deletedNode = null;
let currentNode = this.head;while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode === value) {
deleteNode = currentNode;
if (deleteNode === this.head) {
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.head) {
this.head.previous = null;
}
} else if (deleteNode === this.tail) {
this.tail = this.tail.previous;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
const previousNode = currentNode.previous;
const nextNode = currentNode.next;
previousNode.next = nextNode;
nextNode.previous = previousNode;
}
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return deletedNode;
}
3. 队列
队列是基于链接列表的线性数据结构。队列的字符是它是一个 FIFO(先出)数据结构。
+————+——————+——————-+———-+ | operations | Insert (enqueue) | Delete (dequeue) | Traverse | +————+——————+——————-+———-+ | complexity | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | +————+——————+——————-+———-+
在本节中,我参考Trekhleb的 Github 上的源代码,并用我个人的想法进行一些修改。
JavaScript 中的实现
1.在 JavaScript 中创建队列结构:
我们可以使用链接列表来实现队列。我们将从尾部节点推送新节点,然后从头节点弹出节点。

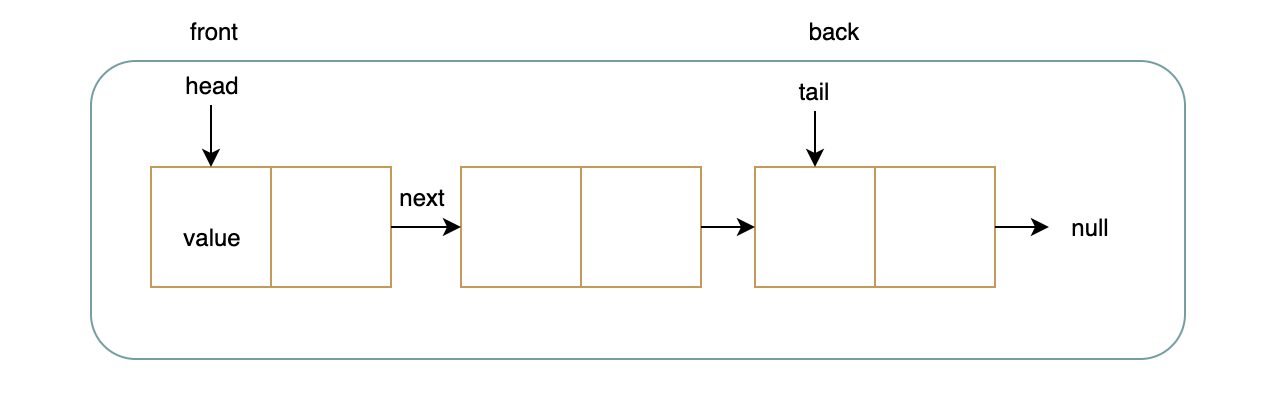
复制right@A莱曼
数据结构的实现:
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
}class Queue {
constructor() {
this.linkedList = new LinkedList();
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.linkedList.head;
}
peek() {
if (!this.linkedList.head) {
return null;
}
return this.linkedList.head.value;
}
}
2. 队列:将新节点添加到尾部节点(背面)

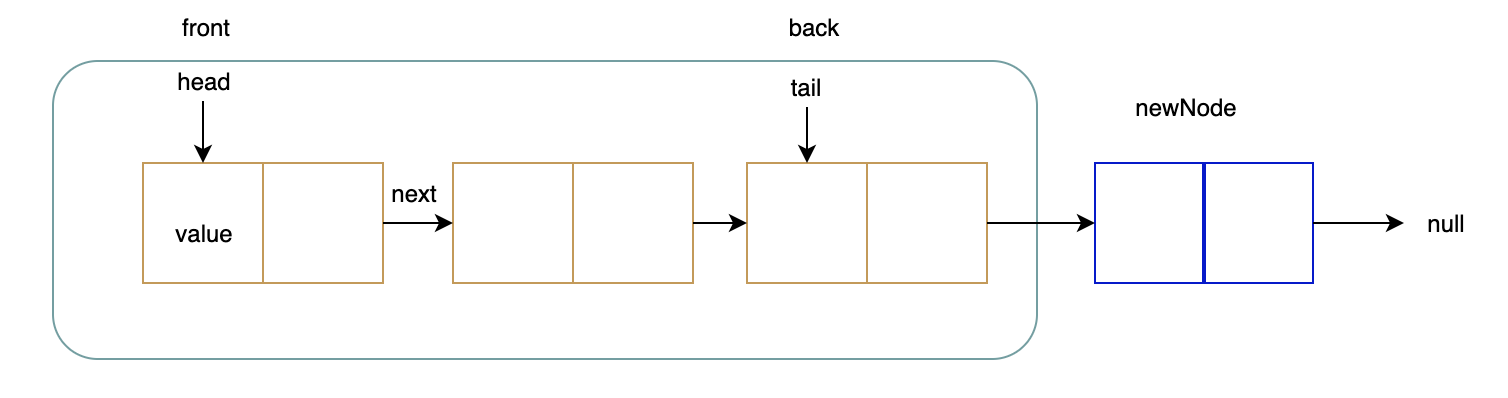
复制right@A莱曼enqueue(value) {
this.linkedList.append(value);
}
3.取消队列:删除链接列表的头节点(正面)
dequeue() {
const removedHead = this.linkedList.deleteHead();
return removedHead ? removedHead.value : null;
}
引用
4. 堆栈
与队列一样,堆栈是基于链接列表的数据结构。堆栈的特性是它是一个 LIFO(最后一个出)数据结构。
+————+——————+——————-+———-+ | operations | Insert (push) | Delete (pop) | Traverse | +————+——————+——————-+———-+ | complexity | O(log 1) | O(log 1) | O(n) | +————+——————+——————-+———-+
在本节中,我参考Trekhleb的 Github 上的源代码,并用我个人的想法进行一些修改。
JavaScript 中的实现
1.在 JavaScript 中创建堆栈结构
我们可以使用链接列表来实现堆栈。我们将从尾部节点推送新节点,然后从头节点弹出节点。

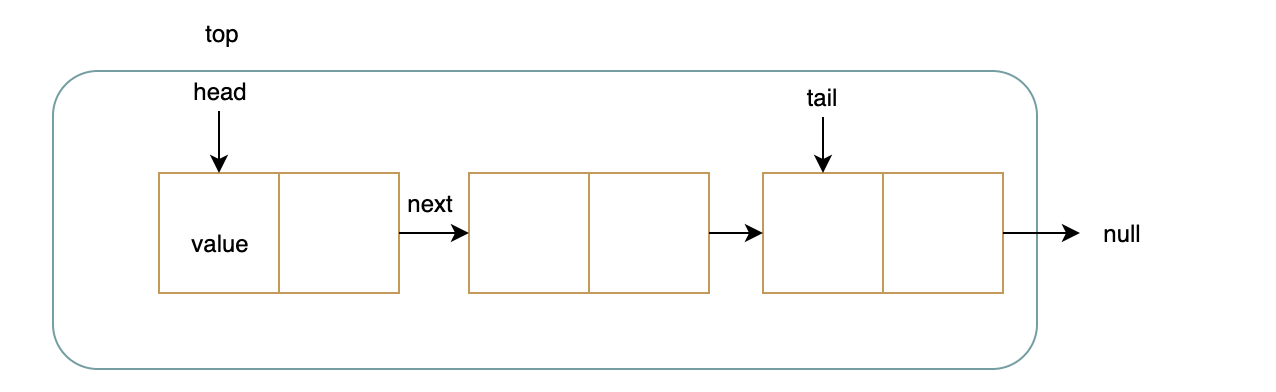
复制right@A莱曼
数据结构的实现:
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
}class Stack{
constructor() {
this.linkedList = new LinkedList();
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.linkedList.head;
}
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return this.linkedList.head.value;
}
}
2.推送:将新节点追加到头节点上链接列表

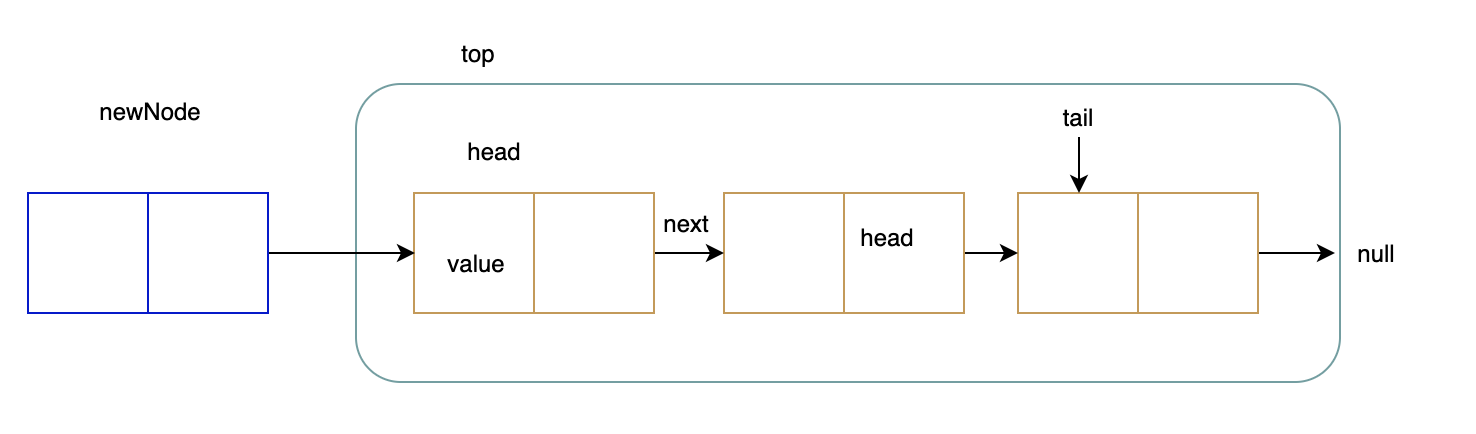
复制right@A莱曼
push(value) {
this.linkedList.prepend(value);
}
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="29692" _msttexthash="78023868">3.弹出:删除链接列表的头节点</font>
pop() {
const removedHead = this.linkedList.deleteHead();
return removedHead ? removedHead.value : null;
}
5.哈希表
哈希表是基于数组的线性数据结构。它是值的关联列表的数组。
+————+—————–+—————–+—————–+ | operations | Insert | Delete | Traverse | +————+—————–+—————–+—————–+ | complexity | O(1) ~ O(n) | O(1) ~ O(n) | O(1) ~ O(n) | +————+—————–+—————–+—————–+
哈希表的优点是允许用户以恒定时间通过索引高效访问数据。
key => lookup “John” => Person(20, “man”) “merry” => Person(22, “woman”) …
它使用哈希键对数据进行索引,并使用不同的类型方法处理冲突问题。
string -> hash code -> indexex. merry-> hash code -> 0hashTable[0] = Person(22, “woman”)
在本节中,我参考Trekhleb的 Github 上的源代码,并用我个人的想法进行一些修改。
哈希函数
- 预哈希: 使用 ASCII 代码将键转换为数字键
- 减少哈希数字以适应表大小
hash(key) {
const hash = Array.from(key).reduce(
(hashAccumulator, keySymbol) => (hashAccumulator + keySymbol.charCodeAt(0)),0,);return hash % this.buckets.length;
}
JavaScript 中的实现
1.在 JavaScript 中创建哈希表
- 使用数组将值存储在不同的链接列表中(链接)
- 将原始键****和值存储到链接列表节点
export default class HashTable {
constructor(hashTableSize = defaultHashTableSize) {
this.buckets = Array(hashTableSize).fill(null).map(() => new LinkedList());
this.keys = {};
}
}

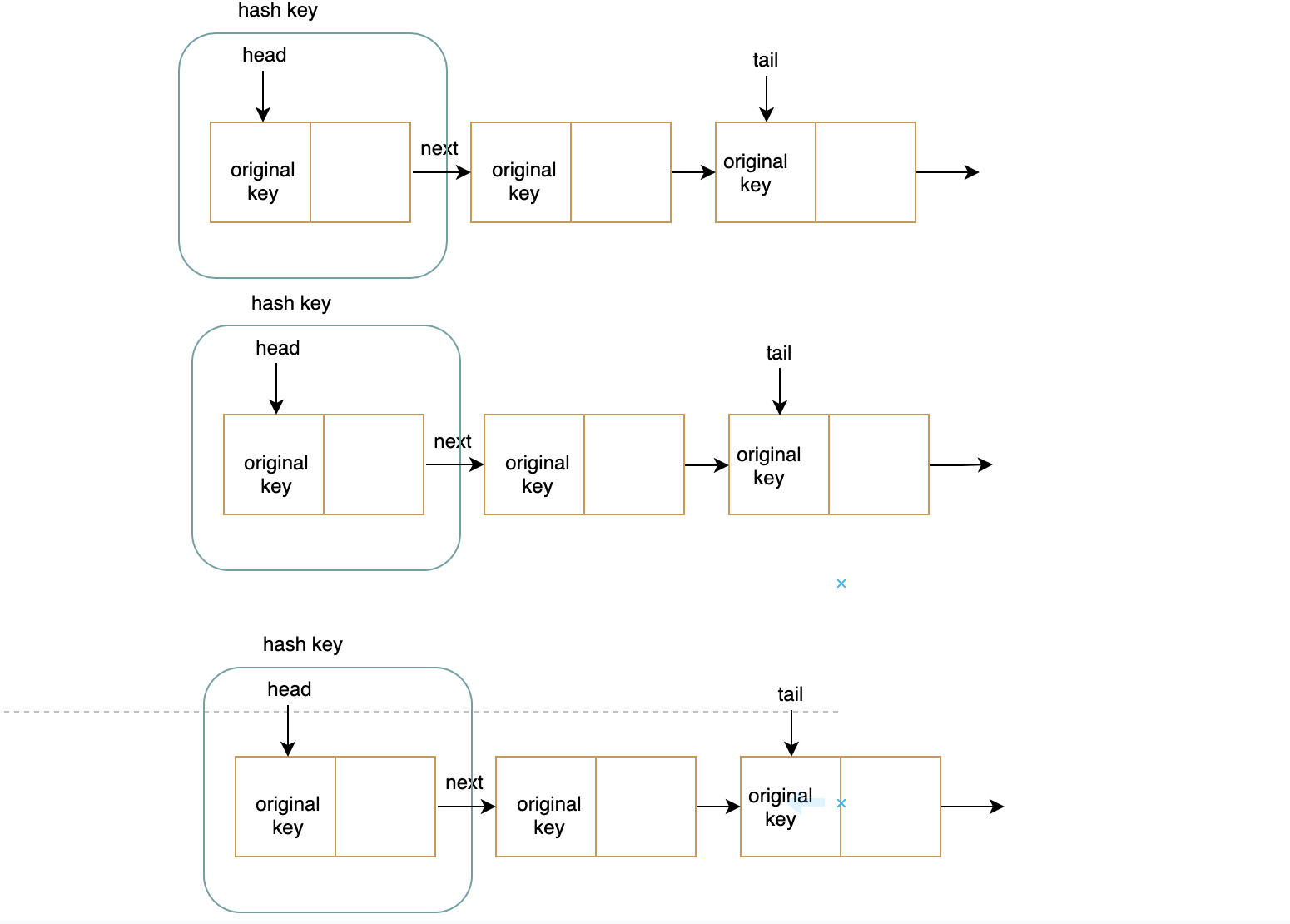
复制right@A莱曼
2. 插入(复杂度:O(1) = O(n))
- 处理哈希冲突:使用链接列表存储具有相同原始密钥的新节点
- 首先,我们使用哈希键来决定要存储哪个存储桶
- 其次,我们使用原始键追加到链接列表中
set(key, value) {
const keyHash = this.hash(key);
this.keys[key] = keyHash;
const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[this.hash(key)];
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key});if (!node) {
bucketLinkedList.append({'key':key, 'value':value});
} else {
node.value.value = value;
}
}
3.搜索(复杂度:O(1) = O(n))
- 首先,我们选择带哈希键的存储桶
- 其次,我们使用原始键搜索链接列表中的值
get(key) {
const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[this.hash(key)];
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key});return node ? node.value.value : undefined;
}
4.删除(复杂度:O(1) = O(n))
- 首先,我们选择带哈希键的存储桶
- 其次,我们使用原始键删除链接列表中的值
delete(key) { const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[this.hash(key)]; const node = bucketLinkedList.find({callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key});return node ? node.value.value : undefined; }
引用
6.二进制搜索树
+————+—————–+—————–+—————–+ | operations | Insert | Delete | Traverse | +————+—————–+—————–+—————–+ | complexity | O(log n) ~ O(n) | O(log n) ~ O(n) | O(log n) ~ O(n) | +————+—————–+—————–+—————–+
在本节中,我参考Trekhleb的 Github 上的源代码,并用我个人的想法进行一些修改。
JavaScript 中的实现
1.在 JavaScript 中创建二进制树结构
- 单个节点具有左子节点、右子节点、父节点和值
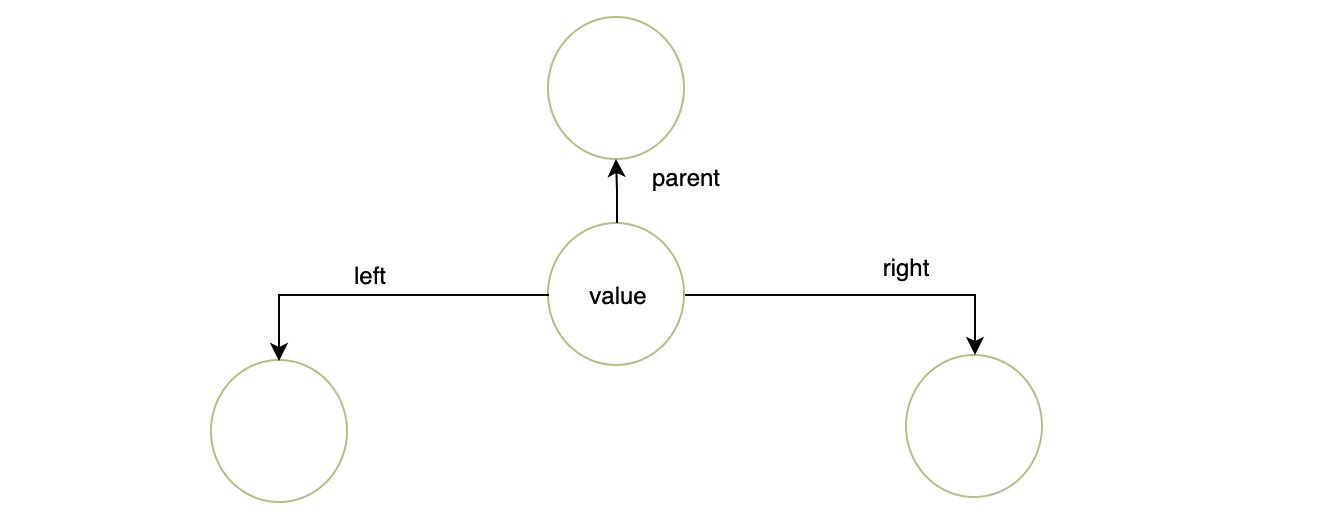
复制right@A莱曼
class BinaryTreeNode {
constructor(value = null) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.parent = null;
this.value = value;
}
setValue(value) {
this.value = value;
return this;
}
setLeft(node) {
if (this.left) {
this.left.parent = null;
}
this.left = node;
if (this.left) {
this.left.parent = this
}
}
setRight(node) {
if (this.right) {
this.right.parent = null;
}
this.right = node;
if (this.right) {
this.right.parent = this
}
}
copy(source, target) {
target.setValue(source.value)
target.setLeft(source.left)
target.setRught(source.right)
}
removeChild(node) {
if (this.left && this.left.value === node.value) {
this.left = null;
return true;
}
if (this.right && this.right.value === node.value) {
this.right = null;
return true;
}
return false;
}
replaceChild(targetNode, newNode) {
if (!targetNode || !newNode) {
return false;
}
if (this.left && this.left.value === targetNode.value) {
this.left = newNode;
return true;
}if (this.right && this.right.value === targetNode.value) {
this.right = newNode;
return true;
}return false;
}
}
2.将新节点插入二进制搜索树(复杂性:O(日志 n) = O(n))
insert(value) {
if (this.value === null) {
this.value = value;
return this;
}if (this.value > value) {
if (this.left) {
return this.left.insert(value)
}
const newNode = new BinaryTreeNode(value);
this.setLeft(newNode);
return newNode;
}if (this.value < value) {
if (this.right) {
return this.right.insert(value)
}
const newNode = new BinaryTreeNode(value);
this.setRight(newNode);
return newNode;
}
return this;
}
3.在二进制搜索树中搜索特定节点(复杂性:O(日志 n) = O(n))
- 检查节点的值。如果值小于目标值,则搜索到左侧节点,反之亦然。
find(targetValue) {
if (this.value === targetValue) {
return this;
}if (this.value > targetValue && this.left) {
return this.left.find(targetValue);
}if (this.value > targetValue && this.right) {
return this.right.find(targetValue);
}return null;
}
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="32357" _msttexthash="221100633">4.在二进制搜索树中搜索最小节点(复杂性:O(n))</font>
findMin() {
if (!this.left) {
return this;
}return this.left.findMin();
}
5.搜索并删除二进制搜索树中的特定节点(复杂性:O(日志 n)= O(n))
remove(value) {
const targetNode = this.find(value);
if (!targetNode) {
return false;
}// Get the parent for removing the child
const { parent } = targetNode;// Check if there are children under the target node
if (!targetNode.left && !targetNode.right) {
// There is no child under the target node
if (parent) {
parent.removeChild(targetNode);
} else {
targetNode.setValue(null);
}
} else if (targetNode.left && targetNode.right) {
const nextBiggerNode = targetNode.right.findMin();
if (nextBiggerNode.value !== targetNode.right.value) {
this.remove(nextBiggerNode.value);
targetNodeToRemove.setValue(nextBiggerNode.value)
} else {
targetNode.setValue(targetNode.right.value);
targetNode.setRight(targetNode.right.right);
}
} else {
// There is only one child the node to remove
const childNode = targetNode.left || targetNode.right;
if (parent) {
// replace the target node with the child
parent.replaceChild(targetNode, childNode);
} else {
// root node
BinaryTreeNode.copy(childNode, targetNode)
}
}
}
性能
1.高度
- 节点的高度表示右子树或左子树的最大深度。
// The height of a node means the max value between the left sub-tree and the right-sub-tree
get height() {
return Math.max(this.leftHeight, this.rightHeight)
}// Get the height of the left sub-tree: the height of the left child node +1
get leftHeight() {
if (!this.left) {
return 0;
}
return this.left.height + 1;
}// Get the height of the right sub-tree: the height of the right child node +1
get rightHeight() {
if (!this.right) {
return 0;
}
return this.right.height + 1;
}
``
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="32969" _msttexthash="7376967">2.平衡</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="32786" _msttexthash="163964957">对于平衡二进制树,左子树之间的高度差应小于或等于 1。</font>
get balanceFactor() {
return this.leftHeight - this.rightHeight;
}
## <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="39195" _msttexthash="5334199">引用</font>
* [类中函数前的"get"关键字是什么?](https://zshipu.com/t?url=https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31999259/what-is-the-get-keyword-before-a-function-in-a-class)
* [吸气](https://zshipu.com/t?url=https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Functions/get)
* [静态](https://zshipu.com/t?url=https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-TW/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Classes/static)
# <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="33553" _msttexthash="13674817">7\. 二进制堆</font>
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="34671" _msttexthash="226369000">堆只是一个树**,具有特殊****属性或**约束其节点的值,称为**堆属性约束**</font>
+------------+----------+----------+----------+-------------------+
| operations | Insert | Delete | Traverse | Heapify down / up |
+------------+----------+----------+----------+-------------------+
| complexity | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(n) | O(log n) |
+------------+----------+----------+----------+-------------------+
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="27352" _msttexthash="266241183">在本节中,我学习实现数据结构从[中断:编程和编码访谈](https://zshipu.com/t?url=https://www.udemy.com/course/break-away-coding-interviews-1/)与轻微的修改。</font>
## <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="38493" _msttexthash="11242634">形状属性</font>
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="34074" _msttexthash="316392375">1.堆中二进制树的每个级别都已填充,除了最后一个。堆应形成一个完整的**二进制树**</font>
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="38974" _msttexthash="85698652">2.按数组**实现。**如果索引 i**有**一个**节点。**</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="37622" _msttexthash="50277539">它在索引时**有一**个左子: **2i = 1**</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="23153" _msttexthash="72227584">它在索引上**有**一个合适的孩子: **2i = 2**</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="27118" _msttexthash="73420646">它在索引**时有**父级: **(i = 1)/2**</font>
export default class Heap { constructor() { this.heapContainer = []; }
getLeftChildIndex(index) {
var leftIndex = 2 * i + 1;
if (leftIndex >= this.heapContainer.length) {
return -1;
}
}getRightChildIndex(index) {
var rightIndex = 2 * i + 2;
if (rightIndex >= this.heapContainer.length) {
return -1;
}
}getParentIndex(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.heapContainer.length) {
return -1;
}
return (index - 1) / 2
}getNode(index) {
if (index < this.heapContainer.length){
return this.heapContainer[index];
} else {
return 'undfined'
}}}
## <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="29549" _msttexthash="7389733">堆属性</font>
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="23725" _msttexthash="19568107">1.最小堆:</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="33319" _msttexthash="67547805">每个节点的值应为_<=_其子节点的值</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="33267" _msttexthash="54792894">值最小的节点应该是树的根</font>
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="33709" _msttexthash="24371464">2.最大堆数:</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="23010" _msttexthash="60319961">每个节点值应为 >= 其子节点的值</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="44226" _msttexthash="59001423">具有最大值的节点应是树的根</font>
## <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="28419" _msttexthash="25170626">JavaScript 中的实现</font>
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="22958" _msttexthash="119023346">1.向下堆(复杂性:每个呼叫的 O(log n)</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="23452" _msttexthash="7486934">最小堆</font>
heapifyDown(index) { var leftIndex = getLeftChildIndex(index), rightIndex = getRightChildIndex(index), smallerIndex = -1;if (leftIndex !== -1 && rightIndex !== -1) { smallerIndex = getNode(leftIndex) < getNode(rightIndex) ? leftIndex : rightIndex; } else if (leftIndex !== -1) { smallerIndex = leftIndex; } else { smallerIndex = rightIndex; }if (smallerIndex === -1) { return }if (getNode(smallerIndex) < getNode(index)) { swap(smallerIndex, index); heapifyDown(smallerIndex); } }
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="34775" _msttexthash="109865301">2.向上(复杂性:每个呼叫的 O(log n)</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="34957" _msttexthash="7486934">最小堆</font>
heapifyUp(index) { var parentIndex = getParentIndex(index); if (parentIndex !== -1 && getNode(index) < getNode(parentIndex)) { swap(parentIndex, index); heapifyUp(parentIndex); } }
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="32825" _msttexthash="103346711">3.插入(复杂度:O(日志 n))</font>
insert(value) {
this.heapContainer.push(value);
this.heapifyUp(this.heapContainer.length - 1);
return this;
}
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="33540" _msttexthash="89319217">4.搜索(复杂性:O(n))</font>
find(value)
const foundItemIndices = [];
for (let itemIndex = 0; itemIndex < this.heapContainer.length; itemIndex++) {
if (value === this.heapContainer[itemIndex]) {
foundItemIndices.push(itemIndex);
}
}
return foundItemIndices;
}
<font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="32890" _msttexthash="112215285">5.删除(复杂性:每个呼叫的 O(log n)</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="24271" _msttexthash="63421384">将目标节点替换为最后一个节点</font>
* <font _mstmutation="1" _msthash="38740" _msttexthash="41318329">向下堆或堆起目标节点</font>
remove(value) { const numberOfItemsToRemove = this.find(value).length; for (let iteration = 0; iteration < numberOfItemsToRemove; iteration ++) { const indexToRemove = this.find(value).pop(); if (indexToRemove === (this.heapContainer.length) - 1) { this.heapContainer.pop(); } else { this.heapContainer[indexToRemove] = this.heapContainer.pop(); }const parentNode = getNode(getParentIndex(iteration)); if (this.getLeftChildIndex(indexToRemove) !== -1 && parentNode !== ‘undefined’) { this.heapifyDown(indexToRemove); } else { this.heapifyUp(indexToRemove); } }return this; }
- 原文作者:知识铺
- 原文链接:https://geek.zshipu.com/post/java/JavaScript%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80%E4%B8%BA%E5%88%9D%E5%AD%A6%E8%80%85%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0-JavaScript-%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84/
- 版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可,非商业转载请注明出处(作者,原文链接),商业转载请联系作者获得授权。
- 免责声明:本页面内容均来源于站内编辑发布,部分信息来源互联网,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或者证实其内容的真实性,如涉及版权等问题,请立即联系客服进行更改或删除,保证您的合法权益。转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。也可以邮件至 sblig@126.com


